1、What is "PVC waterproofing membrane"?
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), referred to as PVC in English, is an organic polymer compound that can be said to be everywhere in life. For example, the plastic cups, plastic bags, various water pipes, wire pipes, etc. that we often use are mostly made of PVC as raw materials. The most common PVC products used in the construction field are various types of pipes, cables, and waterproofing membranes.

Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) waterproofing membrane in the category of polymer waterproofing membranes is a sheet-like waterproofing membrane made of polyvinyl chloride resin as the main raw material, which is mixed with an appropriate amount of modifiers, antioxidants, ultraviolet absorbers, colorants, fillers, plasticizers, etc., and then processed by kneading, extrusion calendering and other processes.
This type of waterproof membrane can be divided into the following five types: homogeneous PVC waterproof membrane (Type H), PVC waterproof membrane with fiber backing (Type L), fabric-reinforced PVC waterproof membrane (Type P), glass fiber-reinforced PVC waterproof membrane (Type G), and glass fiber-reinforced PVC waterproof membrane with fiber backing (Type GL). Type H PVC waterproof membrane is a smooth sheet with no reinforcing material inside and no backing material outside.

2.Application advantages of the material itself
Application cases of waterproof engineering


Polyvinyl chloride waterproofing membrane is a kind of polymer waterproofing membrane. At present, there are three mainstream polymer waterproofing membranes: EPDM waterproofing membrane, PVC waterproofing membrane, and TPO waterproofing membrane. The application indicators of EPDM waterproofing membrane are excellent, but there is one defect: poor weldability. Due to its material properties, the welding performance is poor. In the current construction application of EPDM waterproofing membrane, the overlap seam treatment is mostly overlapped by gluing. As time goes by, the adhesive or adhesive tape will age and fail, and the overlap edge will fall off, which will lead to the failure of the overall waterproof layer. Ps: There are special adhesives for EPDM overlap edge treatment abroad, and the service life can be comparable to that of the membrane, but its price is more expensive, and this product process has not yet been followed up in China.
Thermoplastic polyolefin (TPO) waterproofing membrane is a new generation of polymer waterproofing materials. Its application performance indicators are also very good, comparable to EPDM. However, due to its late launch, the various processes and methods for producing TPO in China are not yet stable and mature, and the cost of use is higher, so its application rate in the domestic market is slightly lower.
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) waterproofing membrane can be said to be the leader in the field of polymer membranes due to its good weldability, mature research and development, production process and supporting construction methods. Its domestic market application rate ranks first among the three (PVC/TPO/EPDM).

Among the three optional polymer waterproofing materials listed in the single-layer roof system specification, the application advantages of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) waterproofing membrane are also very obvious: it can be exposed for use, energy saving, reducing the overall cost, ensuring the quality of long-term waterproofing projects, etc. Therefore, polyvinyl chloride waterproofing membrane can be used in some construction sites with strict requirements on material performance. For example, in the large-span metal or concrete structure roofs of major factories, warehouses, etc., it can be used as a waterproof layer in such sites and play a good waterproofing effect.

Note
In the national engineering technical specification for single-layer roof waterproofing system: "JGJ/T316-2013 Single-layer waterproofing membrane roof engineering technical specification", a total of five types of waterproof membranes are selected, namely: thermoplastic polyolefin waterproof membrane (TPO), polyvinyl chloride waterproof membrane (PVC), ethylene propylene rubber waterproof membrane (EPDM), elastomer modified asphalt waterproof membrane (SBS), plastomer modified asphalt waterproof membrane (APP).
3、Introduction to the construction and application of materials
(I) Construction methods of large-surface roll materials:
There are several large-surface construction methods for PVC waterproof roll materials: ① Mechanical fixing method; ② Adhesive method; ③ Empty laying (top pressing) method.
① Mechanical fixing method:
The mechanical fixing method is a construction method that uses special fixing parts to fix the roll material on the base layer (can be divided into point fixing and linear fixing). It is commonly used in some steel structure roofs, light steel roofs, etc.

② Adhesive method:
The adhesive method is not difficult to understand. During construction, the adhesive is applied to the roll material and the base surface, and the roll material is bonded and fixed to the base surface through the adhesive. This construction method is often used in the waterproof construction of some concrete structure layers. The bonding method can be divided into full bonding method, strip bonding method and point bonding method, which is to apply adhesive in local strip or point areas to carry out the bonding construction of the roll material;

③ Empty laying (top pressing) method:
The empty laying method is that the adhesive is not applied to the whole large surface, and only the edge of the construction base surface is bonded and fixed within a certain range (generally 800mm), and the material is pressed on the top, which is often used in some concrete structure roofs and other parts.

(II) Overlap hot air welding construction method:
The above three large-surface construction methods are slightly different, but the treatment method of the overlap edge of the coil is unified: hot air welding method. This type of welding method is non-contact welding. It is heated by the welding machine and blows out hot air with a certain wind pressure strength. The upper and lower coils of the overlap surface are heated to a molten state, and then compacted and fused by rollers and other tools to achieve the welding result.

Commonly used hot air welding machines include but are not limited to: manual hot air welding guns, automatic hot air welding machines, etc.

Hot air welding methods are also divided into two categories according to the number of welds: single seam welding and double seam welding. Single seam welding method is often used in the construction of some single-layer roofs, underground buildings and other civil engineering projects; double seam welding method is often used in the construction of some municipal, road and bridge projects such as tunnels, artificial lakes, and landfills.
In GB50108-2008 Technical Specification for Waterproofing of Underground Projects, there are different regulations for the overlap width of the two welding methods: single-seam welding requires an overlap of at least 60mm, of which the actual welding width is not less than 30mm; double-seam welding requires an overlap of at least 80mm, of which the actual welding width is 10*2+cavity (width 10-20mm).

Tips: To check whether the weld is firm, a hook is usually used to hook and pull along the weld one by one. If the hook can penetrate into the weld at a certain point, it means that there is a false weld or leaking weld at that place, and timely repair welding is required; to check the weld width, the strip cutting method is used, and the strip is cut perpendicular to the weld to observe whether the actual welding width of the cross section is reached.

(III) Common node processing methods:
① T-type lap joint: T-type lap joint is the key point of water leakage. If there is a part that is not heated properly during welding, it will cause false welding or leaking welding. The processing method is to scrape the edges of the T-type lap joint flat with a scraper (the national standard 1.5mm thick material must be scraped flat), and then perform solid welding.

② Yin-yang corner welding: There are a large number of corners such as yin-yang corners in actual construction. When constructing such parts, you must pay attention to welding the turning points, folding corners, and cutting points firmly to avoid leakage from such parts.

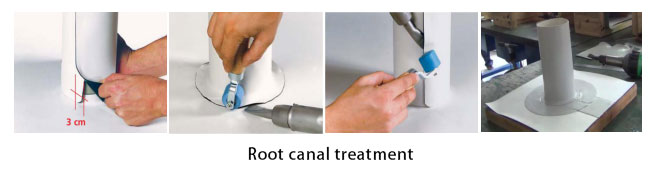
③ Welding at the root of the pipe: The root of the pipe is a detail node that requires special attention in actual construction applications because of its horizontal and vertical intersection and the need for three-dimensional cutting and enclosing of the pipe.
④ Welding of water outlet: Due to long-term water accumulation at the water outlet, and a certain gap between the water outlet components and the structure, it is also a detailed node part where leakage frequently occurs in actual construction applications.
